This Day, That Year: Sept 3


Editor's note: This year marks the 70th anniversary of the founding of New China.
China has been launching polar and geosynchronous orbit meteorological satellites since 1988.
On Sept 3, 1990, the country's second Fengyun-1 experimental satellite was launched as seen in the item from China Daily.
Over the past 50 years, 16 weather satellites from the Fengyun series were launched and eight of them are functioning and detailing meteorological situations in China and around the world.
Weather satellites are used to monitor natural phenomena such as typhoons and storms, and to provide meteorological information for studying global climate change.
Fengyun satellites have played an effective role in providing information on natural disasters for countries involved in the Belt and Road Initiative-an infrastructure and trade network connecting Asia with Europe and Africa along ancient trade routes-in the past year.
Information and data garnered by these satellites are available to about 90 countries and regions around the globe, as well as 2,600 users in China, according to statistics from China Meteorological Administration.
By 2025, the country plans to send 11 more meteorological satellites into orbit to further improve its weather forecasting accuracy and ability to cope with natural hazards, according to China National Space Administration.
The planned satellites include three Fengyun-3 satellites in polar orbit, two Fengyun-4 satellites in geostationary orbit, a dawn-dusk orbit climate satellite, a high-precision greenhouse gas detection satellite and a hyperspectral satellite.
China also aims to send a microwave detection satellite into the geostationary orbit to enhance its ability to predict and monitor fast-changing typhoons, rainstorms and other extreme weather. The satellite will work with the Fengyun-4 series to improve forecasting of rainfall and climate.
A precipitation radar measurement satellite is also planned to improve the accuracy of numerical forecasting of precipitation.
Scientists and engineers also started work on the Fengyun-5 and 6 series.
- Beijing's iconic museums close as rainstorms batter city
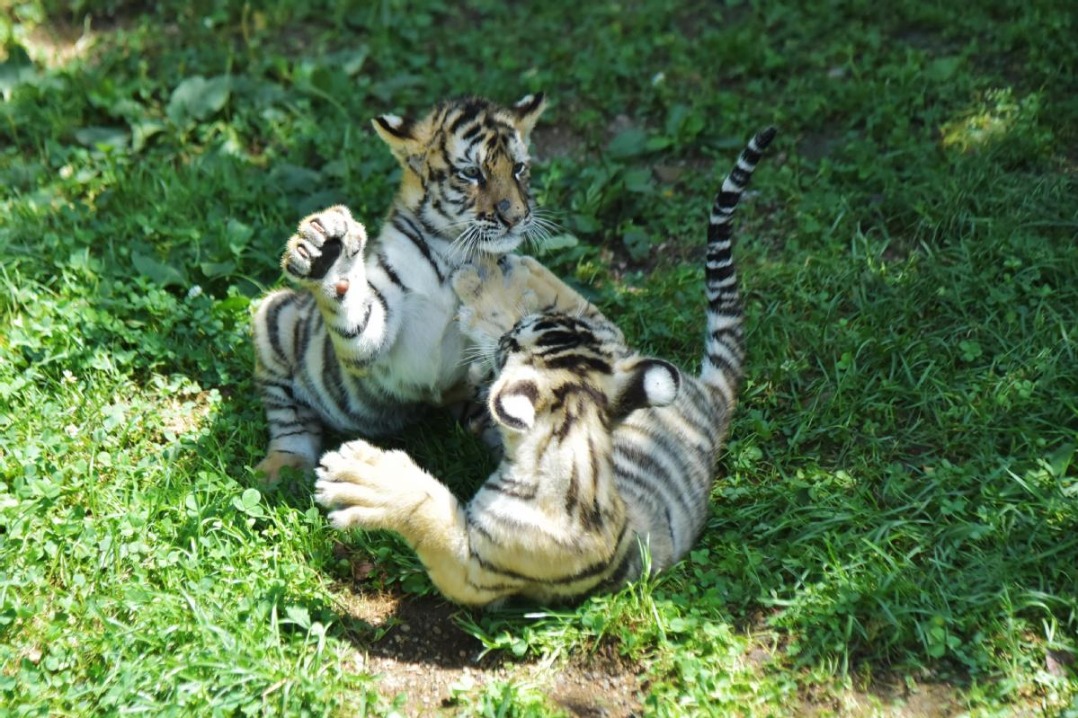
- Siberian tiger cubs play at park in Mudanjiang, NE China
- Guangdong moves swiftly to combat Chikungunya
- Senior CPC official attends forum on boosting cultural strength
- World's first robot 6S store opens in South China's Shenzhen
- Wind power transforms life on roof of the world